Market Structure
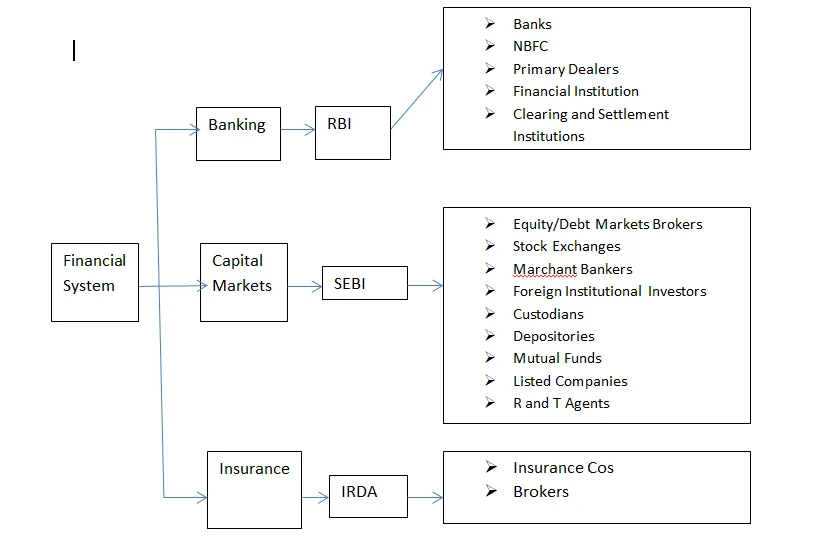
The Indian Financial System is a comprehensive system created to mobilize capital from diverse sectors of the economy and distribute it to sectors that require it. This process is aided by a range of enterprises known as financial intermediaries that offer a variety of products and services. Banks, insurance companies, and mutual funds are just a few examples.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which was established by an Act in 1935, regulates India’s banking sector. In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) serves as both a monetary authority and a bank supervisor.
Structure of Market:
Banks
Commercial banks, co-operative banks, development banks, regional rural banks, payment banks, small finance banks, and local area banks are the different types of banks in India. Commercial banks are divided into three categories: public, private, and foreign banks (operating in India). For all of these banks to open and operate branches in India, they must first obtain a license from the Reserve Bank of India. All banks must comply with RBI regulations on an ongoing basis after they begin operations.
Co-operative banks
Co-operative banks are divided into two categories: urban co-operative banks and others. Urban Co-operative Banks are controlled by both the state government and the Reserve Bank of India. NABARD, on behalf of the RBI and the respective state governments, supervises other cooperative banks. Multi-state cooperative banks, on the other hand, are subject to both the Central Government and the RBI’s jurisdiction.
Scheduled Banks and Non-scheduled Banks
Scheduled Banks and Non-scheduled Banks are the two types of banks that operate in India. A scheduled bank is one that is listed in the 2nd schedule of the RBI Act. It is required to adhere to certain reserve requirements, such as the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), in relation to its Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL), such as deposits, submission of specified periodic returns, and maintenance of specified books of account. They can also borrow money from the RBI in certain instances.
NBFCs
RBI regulates non-banking financial companies (NBFCs). The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) allows depositors to raise funds. These are also permitted to lend on leasing, hire-purchase, bill discounting, and other similar arrangements.
Payment banks
Payment banks and small finance banks are two new types of banks that have lately entered the market. While payment banks are not permitted to provide loans, only they are permitted to accept deposits. They can make deposits of up to one lakh rupees. Their primary role is to collect and settle debts. Small finance banks are a subset of niche financial institutions. Small Finance Banks can offer basic banking services such as deposit acceptance and lending. They must meet the banking demands of the populace, which previously had no access to banking. Furthermore, they must have a minimum of Rs. 100 crore in capital.
Primary Dealers
Primary Dealers (PDs) are mainly involved in the primary and secondary markets for the purchase and sale of government securities. To maintain the required level of SLR, all banks must invest in government securities, according to RBI regulations. As a result, the PDs are linked to the banking system.
Development Banks
In addition to the banks mentioned above, the Government of India has established a few All-India Financial Institutions called Development Banks under distinct Acts. SIDBI, IIFCL, Mudra, NABARD, EXIM, IFCI, Tourism, Finance Corporation of India are some examples. These organizations help industry, exports, agriculture, tourism, and infrastructure by giving long-term funds.
Suggested Reading: RBI & Its Basic Functions – Banking [Notes GK]
The clearing and settlement system in India is another area of the financial market that is regulated and administered by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve Bank of India established the Clearing Corporation of India to undertake some of the clearing and settlement functions.
Download a copy of Market Structure of Commercial Banks in India by M.K. Sharma and H.K. Bal.
